TagRFP-C1 Cloning Vector (Cytoplasm)
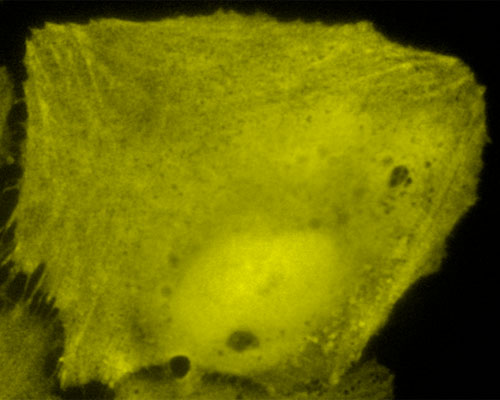
TagRFP is a monomeric orange fluorescent protein derived via site-directed mutagenesis from TurboRFP, a dimeric protein originally cloned from the sea anemone Entacmaea quadricolor. TagRFP exhibits excitation and emission peaks at 555 nanometers and 584 nanometers, respectively, and is well tolerated as a fusion partner for a variety of proteins expressed in mammalian cells. Illustrated in the digital image above is a TagRFP-C1 cloning vector expressed throughout the cytoplasm in a sample of mammalian cells. The cytoplasm of most cell types consists of at least 80 percent water, but the cellular material contains many other substances as well, such as proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, and ions.



