Mouse Brain Tissue
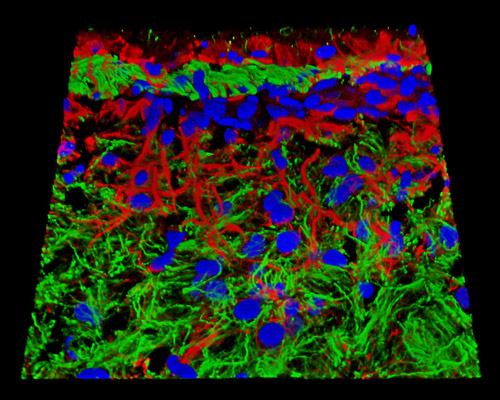
The digital image featured above is a three-dimensional horizontal reconstruction of a 20-micrometer section of mouse brain tissue that was labeled for histones (blue fluorescence), neurofilaments (green), and GFAP (red) with Alexa Fluor probes. Histones are a group of strongly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that are involved in the regulation of genes, physical and functional changes in chromatin during mitosis, and DNA transcription. Neurofilaments, which are intermediate filaments specific to neurons, are believed to essentially play a structural role, however, various studies show they may also function to contribute in the intracellular transport of metabolites. GFAP, or glial fibrillary acidic protein, is a type III intermediate filament protein that plays an important structural role in the star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes as well as a number of ependymal cells.