Rat Smooth Muscle Tissue
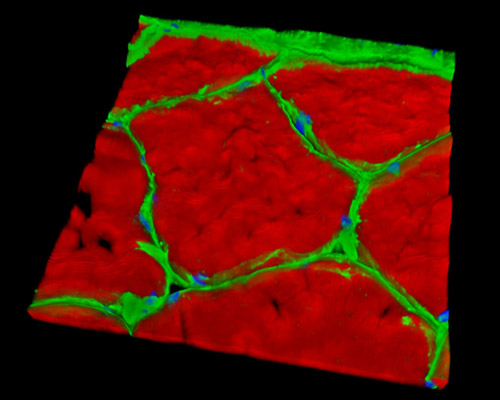
This three-dimensional reconstruction depicts a 16-micrometer section of rat smooth muscle tissue stained with Alexa Fluor 488 (wheat germ agglutinin; highlighting lectins), Alexa Fluor 568 (phalloidin; labeling actin filaments), and DAPI (nuclei). Although there have been many strides forward in understanding smooth muscle and the details of its physiology, there remains a great deal to be learned. Studies of animal models, especially rodents, play a large part in modern examinations of smooth muscle and other tissues. Some recent studies involving mouse smooth muscle tissue have focused on oxidative responses of cells, intracellular calcium mobilization, mapping of the calponin gene, and the expression of myosin heavy chain isoforms.