Mouse Duodenum Tissue - 40x
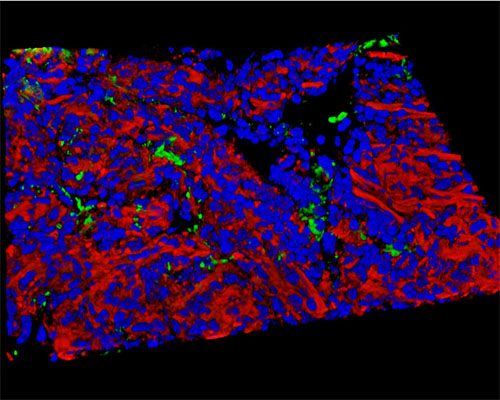
The three-dimensional reconstruction shown above depicts a sample of mouse duodenum tissue stained with Alexa Fluor 350 (wheat germ agglutinin; lectins), Alexa Fluor 568 (phalloidin; actin), and SYTOX Green (nuclei). One of the distinguishing features of the duodenum is the presence of Brunnerís glands. Named for Johann Conrad Brunner, who first described them in the late 17th century, Brunnerís glands are tubular glands located in the submucosa that primarily function in the production of mucus secretions. These secretions are extremely alkaline and are important for lubricating the walls of the intestines and changing the pH level of the chyme, which is acidic when it first enters the duodenum from the stomach.